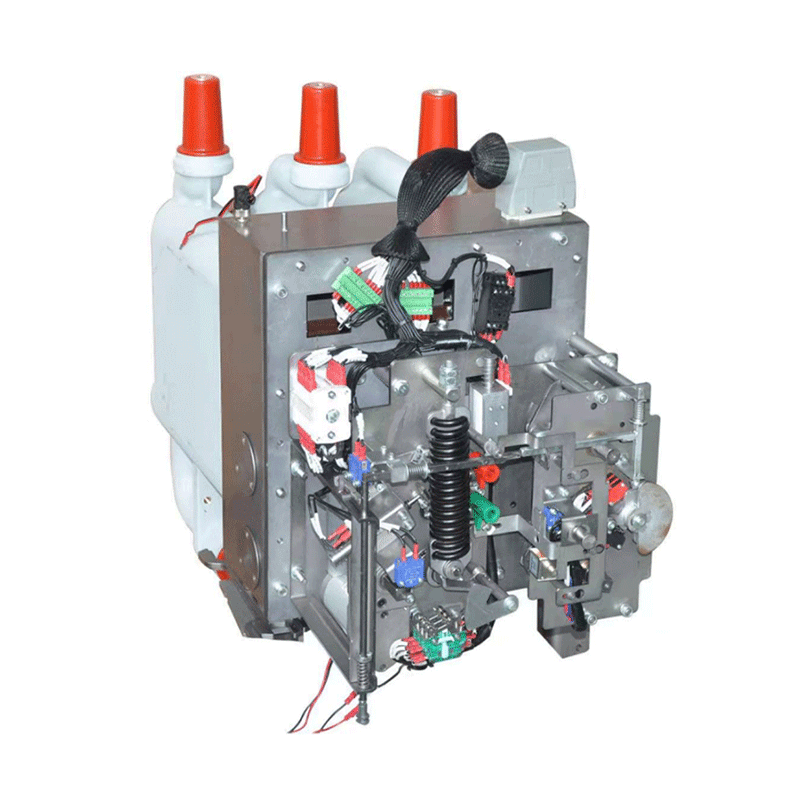
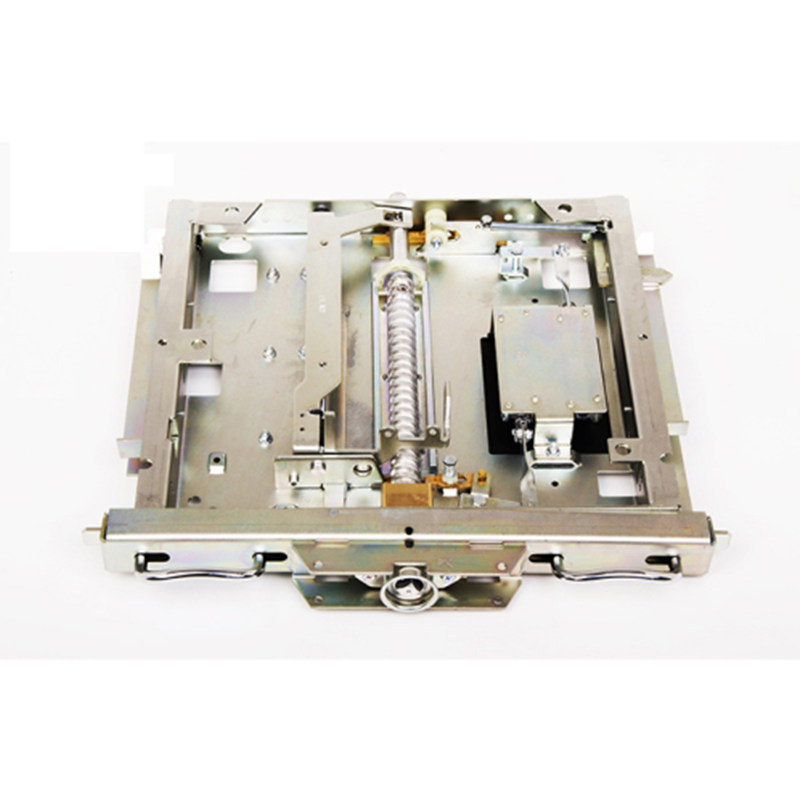
Key Components of a Disconnector Mechanism and Their Functions
In the realm of electrical power systems, disconnector mechanisms play a vital role in ensuring the safe operation and maintenance of electrical equipment. Understanding the key components of a disconnector mechanism and their functions is essential for both electrical engineers and those involved in power system management.
Contact Assembly
The contact assembly is one of the most fundamental components of a disconnector mechanism. It consists of fixed contacts and moving contacts. When the disconnector is in the closed position, the moving contacts firmly engage with the fixed contacts, allowing for the smooth flow of electric current. These contacts are typically made of highly conductive materials such as copper or copper - alloy. Their main function is to establish and break the electrical connection in the circuit. During normal operation, they conduct current without significant resistance. However, when it is necessary to isolate a part of the electrical system for maintenance or in case of a fault, the moving contacts are separated from the fixed contacts, interrupting the current flow.
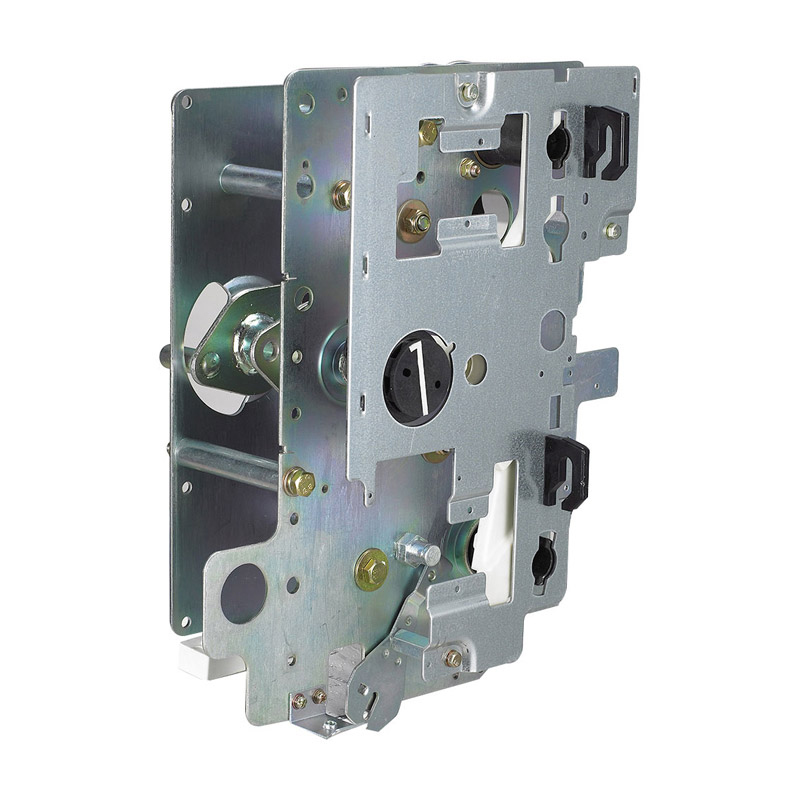
Operating Mechanism
The operating mechanism is responsible for controlling the movement of the moving contacts. There are different types of operating mechanisms, including manual, motor - driven, and pneumatic or hydraulic - operated mechanisms. Manual operating mechanisms are commonly used in low - voltage and some medium - voltage applications. They require direct human intervention to open or close the disconnector. Motor - driven operating mechanisms, on the other hand, are more suitable for high - voltage disconnectors or in situations where remote operation is necessary. These mechanisms use electric motors to drive the movement of the contacts, which can be controlled from a control room. Pneumatic or hydraulic - operated mechanisms are often employed when a large amount of force is required to move the contacts, such as in high - voltage, high - current applications.
Insulating Support
Insulating support components are crucial for maintaining the electrical isolation of the disconnector. They separate the conductive parts of the disconnector from the ground and from each other. Insulating materials such as porcelain, epoxy resin, or composite materials are used for these supports. The insulating support not only provides mechanical support to the contact assembly and other components but also ensures that no electrical leakage occurs. In high - voltage applications, the design and quality of the insulating support are of utmost importance to prevent electrical breakdowns, which could lead to serious safety hazards and power outages.
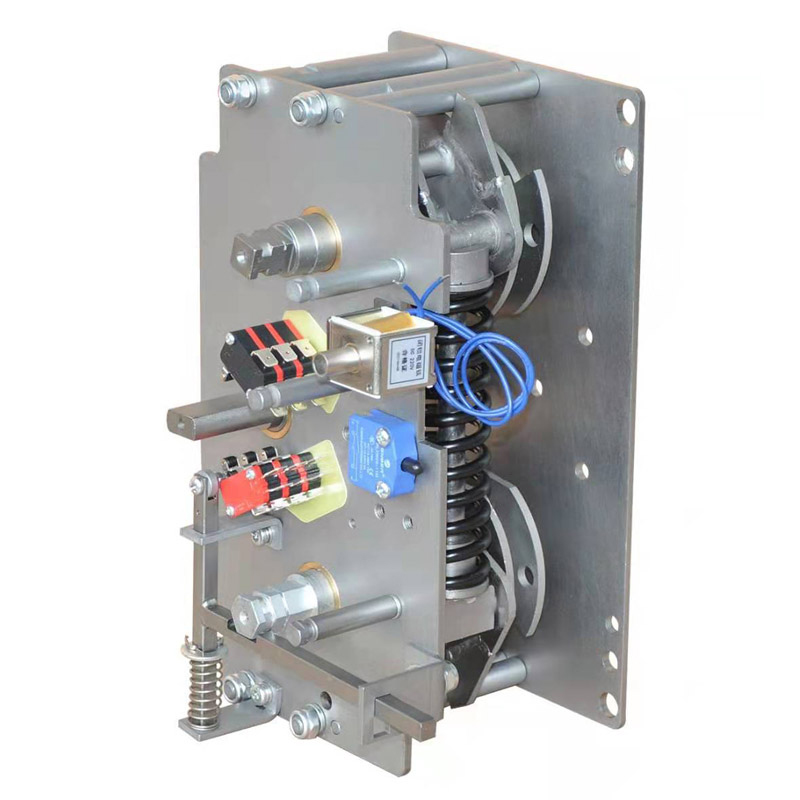
Auxiliary Switch and Interlock Devices
Auxiliary switches are an integral part of the disconnector mechanism. They provide feedback on the position of the disconnector, whether it is open or closed. This information is then transmitted to the control system, allowing operators to monitor the status of the disconnector. Interlock devices, on the other hand, are designed to prevent incorrect operation of the disconnector. For example, they can prevent the disconnector from being opened while there is still current flowing in the circuit, or they can ensure that other related equipment is in a safe state before the disconnector can be operated. These safety features are essential for protecting both the equipment and the personnel working on the electrical system.
In conclusion, the key components of a disconnector mechanism, including the contact assembly, operating mechanism, insulating support, and auxiliary switch and interlock devices, all work in harmony to ensure the proper functioning and safety of the disconnector in electrical power systems. Each component has its unique function, and any malfunction or improper design of these components can have significant consequences for the reliability and safety of the entire power system.



.jpg)