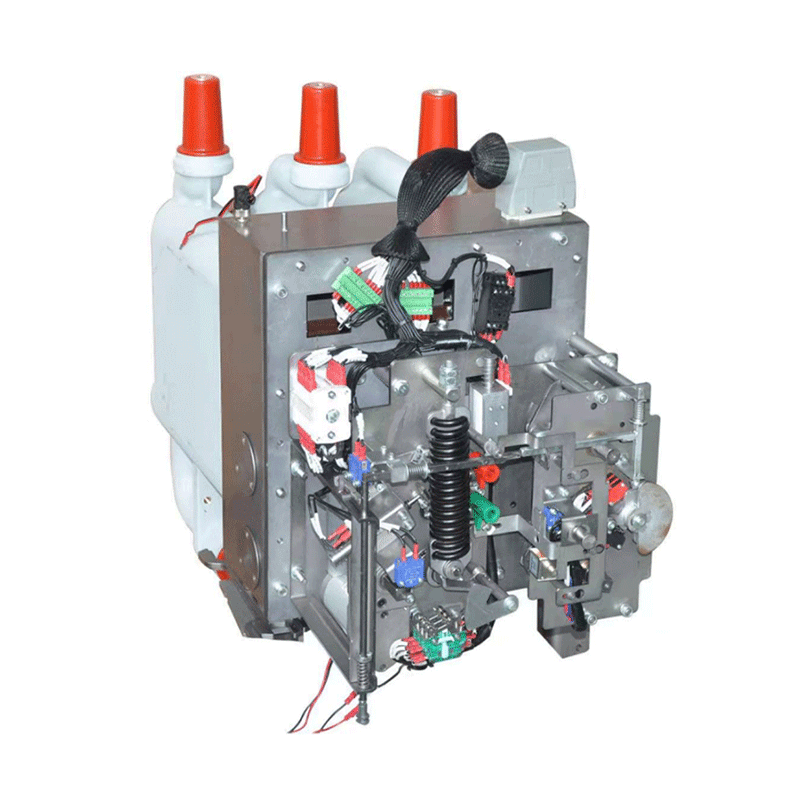
What is the function of the isolator circuit breaker?
The isolator circuit breaker serves a dual function in electrical systems, combining the roles of a circuit breaker and an isolator. Isolators are designed to physically separate a section of an electrical circuit during maintenance, repairs, or to ensure safety, while circuit breakers automatically safeguard the system from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.Here's a detailed breakdown of its functions:
Circuit Protection:
1. Normal Circuit Interruption
Function: Operates manually or remotely to connect or disconnect power under normal load conditions.
2. Fault Protection
Function: Automatically disconnects the circuit during faults to prevent damage to equipment and safety hazards.
Electrical Isolation
1. Physical Disconnection: Provides a visible or verified physical break to isolate a section of the circuit from the power source during maintenance or repairs.
2. Safety Assurance: The isolation feature guarantees that no current can flow, even if the breaker's internal contacts were to accidentally close, due to the physical separation. This protects personnel from electric shock.
Operational Efficiency:
Combined Device: By integrating isolation and circuit-breaking functions, it eliminates the need for a separate isolator switch, simplifying system design and saving space in electrical installations.
Applications of Solid Isolated Circuit Breaker
1. Renewable Energy Systems: For protecting inverters, transformers and grid connections in renewable energy plants. The solid insulation of the Solid Isolated Circuit Breaker withstands harsh outdoor conditions.
2. Industrial Facilities: Protect motors, transformers, and critical machinery from overloads and short circuits in environments with dust, humidity, or chemical exposure.
3. Transportation Infrastructure: Deployed in traction power supply systems and substations to ensure uninterrupted, safe rail operations.
Summary: Solid insulated circuit breakers are versatile solutions for modern power systems, combining reliability, environmental compliance, and adaptability to demanding environments. Their applications span from urban grids to renewable energy and industrial automation, making them critical for sustainable infrastructure development.


.jpg)