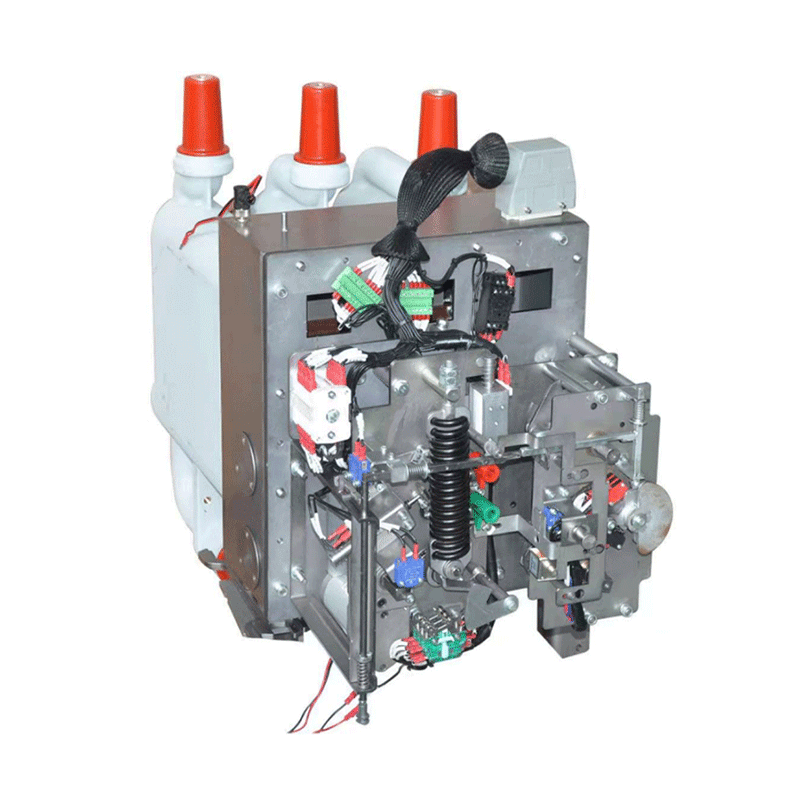
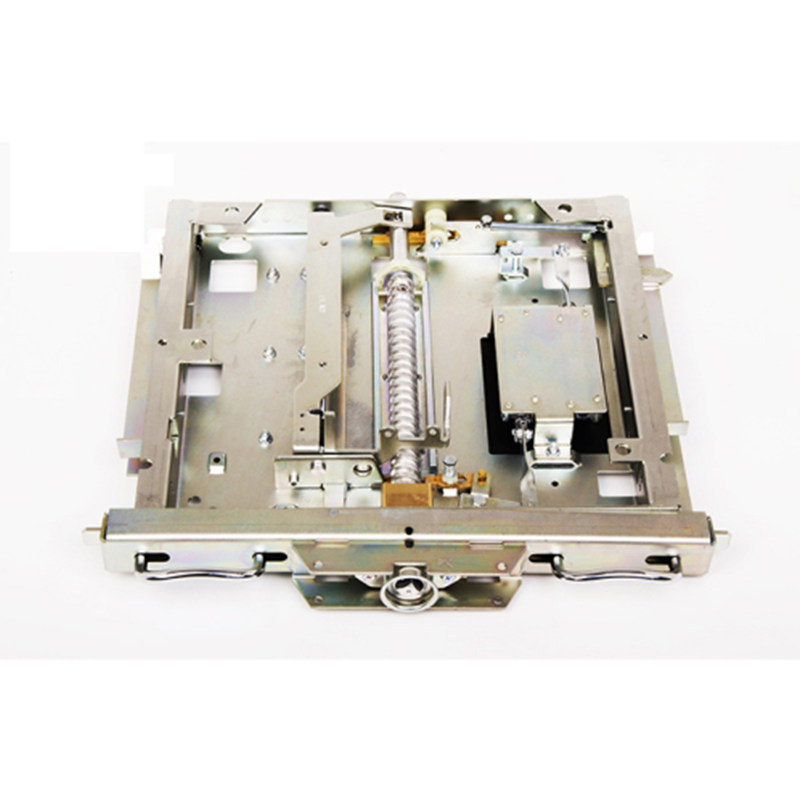
Maintenance Requirements for Disconnector Mechanism
The disconnector mechanism plays a crucial role in numerous electrical systems. To ensure its stable and reliable operation and extend its service life, proper maintenance is of vital importance. The following are the detailed maintenance requirements:
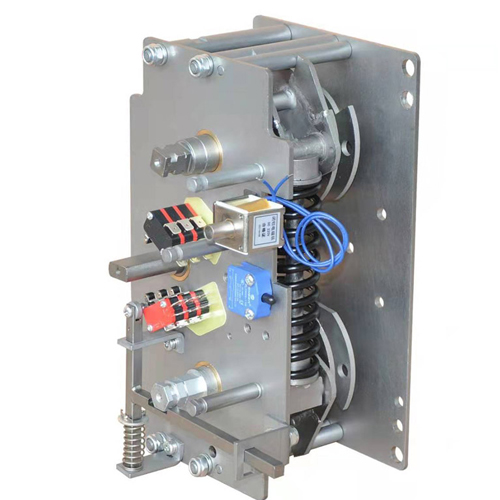
I. Regular Inspection
Exterior Inspection
Check whether there are any signs of damage, deformation, or corrosion on the housing of the mechanism. If cracks are found on the housing, the internal components may be exposed to harsh environments, increasing the risk of malfunctions. For example, if rust appears on the metal housing, it should be removed promptly and protective measures, such as applying anti-rust paint, should be taken.
Examine the connecting parts, including bolts and nuts, to see if they are loose. Loose connections may lead to poor contact, which can cause overheating and even trigger electrical fires. Regularly use appropriate tools to check and tighten the connecting parts to ensure a firm connection.
Contact Inspection
Check the wear of the contacts. Frequent opening and closing operations will gradually wear down the contacts. When the wear of the contacts exceeds the specified limit, it will affect the electrical conductivity and the reliability of the opening and closing operations. The degree of wear can be judged by measuring the thickness of the contacts or observing the smoothness of their surfaces. Replace them if necessary.
Observe whether there are dirt, oxide layers, or burn marks on the surface of the contacts. Dirt and oxidation will increase the contact resistance of the contacts, resulting in overheating. Slight dirt can be wiped off with a clean, soft cloth, while severe oxidation or burn marks require professional repair or replacement.
II. Cleaning Requirements
External Cleaning
Use a dry, lint-free soft cloth to regularly wipe the surface of the mechanism's housing to remove dust, oil stains, and other impurities. Prevent dust from accumulating to avoid affecting heat dissipation, as oil stains may corrode the housing material. For stubborn stains that are difficult to wipe off, a mild cleaner can be used, but make sure that the cleaner does not enter the interior of the mechanism.
Clear the debris around the mechanism to keep the operating space unobstructed. Avoid debris blocking the normal operation of the mechanism and reduce the risk of electrical faults such as short circuits caused by debris.
Internal Cleaning
Under the guidance of professionals, regularly clean the interior of the mechanism. A compressed air gun can be used to remove dust inside, but pay attention to controlling the air pressure to avoid damaging the precision components inside. For internal parts with oil stains, use a special electrical equipment cleaner for cleaning and make sure that the cleaner has completely evaporated before reassembling.
III. Lubrication Measures
Lubrication of Moving Parts
Regularly lubricate the hinges, pins, and other moving parts of the mechanism. Select an appropriate lubricant, such as lithium-based grease, to ensure that the moving parts can rotate flexibly, reducing wear and friction. Generally, lubrication operations should be carried out at regular intervals (such as every six months or depending on the equipment's operating conditions).
When applying the lubricant, pay attention to the appropriate amount to avoid excessive lubricant dripping onto other parts, especially onto the contact parts, which may affect the electrical conductivity.
Lubrication of Driving Parts
For electrically or pneumatically driven disconnector mechanisms, lubricate the bearings, gears, and other components of the driving motor according to the requirements of the equipment manufacturer. For example, appropriate amounts of lubricating oil need to be added to the motor bearings at certain operating intervals, and gear grease can be applied to the gears to ensure the smooth operation of the driving system, reducing noise and wear.
IV. Operational Performance Testing
Opening and Closing Operation Testing
Regularly conduct manual and automatic (if applicable) opening and closing operation tests. Check whether the opening and closing actions are smooth and accurate, and whether there are any jams or abnormal noises. If the operation is found to be not smooth, stop the operation immediately and check the cause. It may be due to component wear, poor lubrication, or foreign objects getting stuck.
Test whether the opening and closing times meet the equipment's standard requirements. If the opening or closing time is too long or too short, it may affect the protection performance and normal operation of the electrical system. For example, in the event of a fault, it may not be able to cut off the circuit in time or may trip prematurely due to incorrect operation.
Interlocking Function Testing
Check whether the interlocking function of the mechanism is normal. The interlocking device is set to prevent incorrect operations. For example, the disconnector cannot be closed when the earthing switch is not opened. By simulating different operating conditions, verify the reliability of the interlocking function to ensure that it can effectively prevent incorrect operations under any circumstances and safeguard the safety of personnel and equipment.
V. Environmental Adaptability Maintenance
Moisture-proof Treatment
If the equipment is installed in a humid environment, such as a basement or a coastal area, special moisture-proof measures need to be taken. Desiccant bags can be installed inside the mechanism and replaced regularly to absorb internal moisture. Meanwhile, check the sealing performance of the mechanism to ensure that the housing is well sealed and prevents moisture from entering.
For equipment that has not been in operation for a long time, a comprehensive moisture-proof inspection and treatment should be carried out before it is put back into use to avoid short circuits or corrosion of internal components caused by humidity.
High Temperature and Cold Protection Measures
In a high-temperature environment, pay attention to the heat dissipation of the mechanism. Check whether the cooling fan (if any) is working properly and whether the ventilation ports are unobstructed. If necessary, additional heat dissipation devices can be added or heat insulation measures can be taken to prevent high temperatures from causing component aging and performance degradation.
In cold regions, consider the impact of low temperatures on the materials and lubricants of the mechanism. Some lubricants may become thick or even solidify at low temperatures, affecting the normal operation of the mechanism. Select lubricants suitable for low-temperature environments and take appropriate thermal insulation measures for the mechanism, such as wrapping it with thermal insulation materials.
By strictly following the above maintenance requirements for the disconnector mechanism, its operational reliability can be effectively improved, the probability of malfunctions can be reduced, the safe and stable operation of the electrical system can be ensured, and the service life of the equipment can be extended while reducing operating costs.


.jpg)